Wireless Client and Wireless Access Point Manual
| Document revision: | 2.2 (Tue Jul 18 14:53:58 GMT 2006) |
| Applies to: | V2.9 |
General Information
Summary
This manual discusses management of Atheros and Prism chipset based wireless NICs that comply with IEEE 802.11 set of standards. These interfaces use radio waves as a physical signal carrier and are capable of data transmission with speeds up to 108 Mbps (in 5GHz turbo-mode).
MikroTik RouterOS supports the Intersil Prism II PC/PCI, Atheros AR5000, AR5001X, AR5001X+, AR5002X+, AR5004X+ and AR5006 chipset based cards for working as wireless clients (station mode), wireless bridges (bridge mode), wireless access points (ap-bridge mode), and for antenna positioning (alignment-only mode). For furher information about supported wireless adapters, see Device Driver List
MikroTik RouterOS provides a complete support for IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g wireless networking standards. There are several additional features implemented for the wireless networking in RouterOS - WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), software and hardware AES encryption, WDS (Wireless Distribution System), DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection), Alignment mode (for positioning antennas and monitoring wireless signal), VAP (Virtual Access Point), ability to disable packet forwarding among clients, Nstreme wireless transmission protocol and others. You can see the table of features supported by different cards.
The Nstreme protocol is MikroTik proprietary (i.e., incompatible with other vendors) wireless protocol aimed to improve point-to-point and point-to-multipoint wireless links. Advanced version of Nstreme, called Nstreme2 works with a pair of wireless cards (Atheros AR5210 and newer MAC chips only) - one for transmitting data and one for receiving.
Benefits of Nstreme protocol:
- Client polling. Polling reduces media access times, because the card does not need to ensure the air is "free" each time it needs to transmit data (the polling mechanism takes care of it)
- Very low protocol overhead per frame allowing super-high data rates
- No implied protocol limits on link distance
- No implied protocol speed degradation for long link distances
- Dynamic protocol adjustment depending on traffic type and resource usage
Quick Setup Guide
Let's consider that you have a wireless interface, called wlan1.
-
To set it as an Access Point, working in 802.11g standard, using frequency 2442 MHz and Service Set Identifier test, do the following configuration:
/interface wireless set wlan1 ssid=test frequency=2442 band=2.4ghz-b/g \ mode=ap-bridge disabled=no
Now your router is ready to accept wireless clients.
-
To make a point-to-point connection, using 802.11a standard, frequency 5805 MHz and Service Set Identifier p2p, write:
/interface wireless set wlan1 ssid="p2p" frequency=5805 band=5ghz \ mode=bridge disabled=noThe remote interface should be configured to station as showed below.
-
To make the wireless interface as a wireless station, working in 802.11a standard and Service Set Identifier p2p:
/interface wireless set wlan1 ssid="p2p" band=5ghz mode=station disabled=no
Specifications
Packages required: wirelessLicense required: Level3 (station and bridge mode) , Level4 (station, bridge and AP mode) , CFS (more frequencies)
Submenu level: /interface wireless
Standards and Technologies: IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11g
Hardware usage: Not significant
Related Documents
Description
The Atheros card has been tested for distances up to 20 km providing connection speed up to 17Mbit/s. With appropriate antennas and cabling the maximum distance should be as far as 50 km.
These values of ack-timeout were approximated from the tests done by us, as well as by some of our customers:
| range | ack-timeout | ||
| 5GHz | 5GHz-turbo | 2.4GHz-G | |
| 0km | default | default | default |
| 5km | 52 | 30 | 62 |
| 10km | 85 | 48 | 96 |
| 15km | 121 | 67 | 133 |
| 20km | 160 | 89 | 174 |
| 25km | 203 | 111 | 219 |
| 30km | 249 | 137 | 368 |
| 35km | 298 | 168 | 320 |
| 40km | 350 | 190 | 375 |
| 45km | 405 | - | - |
Please note that these are not the precise values. Depending on hardware used and many other factors they may vary up to +/- 15 microseconds.
You can also use dynamic ack-timeout value - the router will determine ack-timeout setting automatically by sending periodically packets with a different ack-timeout. Ack-timeout values by which ACK frame was received are saved and used later to determine the real ack-timeout.
The Nstreme protocol may be operated in three modes:
- Point-to-Point mode - controlled point-to-point mode with one radio on each side
- Dual radio Point-to-Point mode (Nstreme2) - the protocol will use two radios on both sides simultaneously (one for transmitting data and one for receiving), allowing superfast point-to-point connection
- Point-to-Multipoint - controlled point-to-multipoint mode with client polling (like AP-controlled TokenRing)
The MikroTik RouterOS supports as many Atheros chipset based cards as many free adapter slots are on your system. One license is valid for all cards on your system. Note that maximal number of PCMCIA sockets is 8.
Some chipsets are not stable with Atheros cards and cause radio to stop working. MikroTik RouterBoard 200, RouterBoard 500 series, and systems based on Intel i815 and i845 chipsets are tested and work stable with Atheros cards. There might be many other chipsets that are working stable, but it has been reported that some older chipsets, and some systems based on AMD Duron CPU are not stable.
Only AR5212 and newer Atheros MAC chips are stable with RouterBOARD200 connected via RouterBOARD14 four-port MiniPCI-to-PCI adapter. This note applies only to the RouterBOARD200 platform with Atheros-based cards.
Wireless Interface Configuration
Submenu level: /interface wirelessDescription
In this section we will discuss the most important part of the configuration.
Property Description
ack-timeout (integer | dynamic | indoors) - acknowledgement code timeout (transmission acceptance timeout) in microseconds for acknowledgement messages. Can be one of these:indoors - standard constant for indoor usage
ant-b - use only antenna b
rxa-txb - use antenna a for receiving packets, use antenna b for transmitting packets
txa-rxb - use antenna a for transmitting packets, antenna b for receiving packets
2.4ghz-b/g - IEEE 802.11g (supports also IEEE 802.11b)
2.4ghz-g-turbo - IEEE 802.11g using double channel, providing air rate of up to 108 Mbit
2.4ghz-onlyg - only IEEE 802.11g
5ghz - IEEE 802.11a up to 54 Mbit
5ghz-turbo - IEEE 802.11a using double channel, providing air rate of up to 108Mbit
2ghz-10mhz - variation of IEEE 802.11g with half the band, and, accordingly, twice lower speed (air rate of up to 27Mbit)
2ghz-5mhz - variation of IEEE 802.11g with quarter the band, and, accordingly, four times lower speed (air rate of up to 13.5Mbit)
5ghz-10mhz - variation of IEEE 802.11a with half the band, and, accordingly, twice lower speed (air rate of up to 27Mbit)
5ghz-5mhz - variation of IEEE 802.11a with quarter the band, and, accordingly, four times lower speed (air rate of up to 13.5Mbit)
no-radar-detect - AP scans channel list from "scan-list" and chooses the frequency which is with the lowest amount of other networks detected
radar-detect - AP scans channel list from "scan-list" and chooses the frequency which is with the lowest amount of other networks detected, if no radar is detected in this channel for 60 seconds, the AP starts to operate at this channel, if radar is detected, the AP continues searching for the next available channel which is with the lowest amount of other networks detected
manual-tx-power - channels in configured country only are allowed, but transmit power is taken from tx-power setting
superchannel - only possible with superchannel license. In this mode all hardware supported channels are allowed
no - ssid is included in beacon frames. AP replies to probe-requests with the given ssid ant to 'broadcast ssid' (empty ssid)
ap-bridge - the interface is operating as an Access Point
bridge - the interface is operating as a bridge. This mode acts like ap-bridge with the only difference being it allows only one client
nstreme-dual-slave - the interface is used for nstreme-dual mode
station - the interface is operating as a client
station-wds - the interface is working as a station, but can communicate with a WDS peer
wds-slave - the interface is working as it would work in ap-bridge mode, but it adapts to its WDS peer's frequency if it is changed
short - has a short synchronization field in a wireless packet (56 bits). Is not compatible with 802.11 standard. With short preamble mode it is possible to get slightly higher data rates
both - supports both - short and long preamble
post-2.9.25 - include extensions in the form accepted by MikroTik RouterOS starting from veriosn 2.9.25, and compatible with all known wireless clients
configured - basic and supported-rates settings are used as configured
card-rates - use transmit power, that for different rates is calculated according the cards transmit power algorithm, which as an argument takes tx-power value
default - use the default tx-power
manual-table - use the transmit powers as defined in /interface wireless manual-tx-power-table
dynamic - WDS interfaces are created 'on the fly'
static - WDS interfaces are created manually
Notes
The IEEE 802.11 standard limitation makes it impossible for wireless cards in station mode to work as expected when bridged. That means that if you need to create a bridge, you should not use station mode on that machine. In case you need a bridge on a wireless station, use station-wds mode (may only be used in the AP supports WDS). Bridging on the AP side works fine.
It is strongly suggested to leave basic rates at the lowest setting possible.
Using compression, the AP can serve approximately 50 clients with compression enabled!
Compression is supported only by Atheros wireless cards.
If disable-running-check value is set to no, the router determines whether the network interface is up and running - in order to show flag R for AP, one or more clients have to be registered to it, for station, it should be connected to an AP. If the interface does not appear as running (R), its route in the routing table is shown as invalid! If set to yes, the interface will always be shown as running.
On Atheros-based cards, encryption (WEP, WPA, etc.) does not work when compression is enabled.
The tx-power default setting is the maximum tx-power that the card can use. If you want to use larger tx-rates, you are able to set them, but do it at your own risk! Usually, you can use this parameter to reduce the tx-power.
In general tx-power controlling properties should be left at the default settings. Changing the default setting may help with some cards in some situations, but without testing, the most common result is degradation of range and throughput. Some of the problems that may occur are: (1) overheating of the power amplifier chip and the card which will cause lower efficiency and more data errors; (2) overdriving the amplifier which will cause more data errors; (3) excessive power usage for the card and this may overload the 3.3V power supply of the board that the card is located on resulting in voltage drop and reboot or excessive temperatures for the board.
For different versions of Atheros chipset there are different value range of ack-timeout property:
| Chipset version | 5ghz | 5ghz-turbo | 2ghz-b | 2ghz-g | |||||||
| default | max | default | max | default | max | default | max | ||||
| 5000 (5.2GHz only) | 30 | 204 | 22 | 102 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||
| 5211 (802.11a/b) | 30 | 409 | 22 | 204 | 109 | 409 | N/A | N/A | |||
| 5212 (802.11a/b/g) | 25 | 409 | 22 | 204 | 30 | 409 | 52 | 409 | |||
If the wireless interfaces are put in nstreme-dual-slave mode, all configuration will take place in /interface wireless nstreme-dual submenu, described further on in this manual. In that case, configuration made in this submenu will be partially ignored. WDS cannot be used together with the Nstreme-dual.
Example
This example shows how configure a wireless client.
To see current interface settings:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:34:54:FB arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5213
radio-name="000B6B3454FB" mode=station ssid="MikroTik"
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=2412 band=2.4ghz-b scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=00:00:03
on-fail-retry-time=00:00:00.100 preamble-mode=both
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless>
Set the ssid to mmt, band to 2.4-b/g and enable the interface. Use the monitor command to see the connection status.
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> set 0 ssid=mmt disabled=no \
band=2.4ghz-b/g
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> monitor wlan1
status: connected-to-ess
band: 2.4ghz-g
frequency: 2432MHz
tx-rate: 36Mbps
rx-rate: 36Mbps
ssid: "mmt"
bssid: 00:0B:6B:34:5A:91
radio-name: "000B6B345A91"
signal-strength: -77dBm
tx-signal-strength: -76dBm
tx-ccq: 21%
rx-ccq: 21%
current-ack-timeout: 56
current-distance: 56
wds-link: no
nstreme: no
framing-mode: none
routeros-version: "2.9beta16"
last-ip: 25.25.25.2
current-tx-powers: 1Mbps:28,2Mbps:28,5.5Mbps:28,11Mbps:28,6Mbps:27,
9Mbps:27,12Mbps:27,18Mbps:27,24Mbps:27,36Mbps:26,
48Mbps:25,54Mbps:24
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless>
The 'ess' stands for Extended Service Set (IEEE 802.11 wireless networking).
Nstreme Settings
Submenu level: /interface wireless nstremeDescription
You can switch a wireless card to the nstreme mode. In that case the card will work only with nstreme clients.
Property Description
enable-nstreme (yes | no; default: no) - whether to switch the card into the nstreme modeenable-polling (yes | no; default: yes) - whether to use polling for clientsframer-limit (integer; default: 3200) - maximal frame sizeframer-policy (none | best-fit | exact-size | dynamic-size; default: none) - the method how to combine frames (like fast-frames setting in interface configuration). A number of frames may be combined into a bigger one to reduce the amount of protocol overhead (and thus increase speed). The card is not waiting for frames, but in case a number of packets are queued for transmitting, they can be combined. There are several methods of framing:best-fit - put as much packets as possible in one frame, until the framer-limit limit is met, but do not fragment packets
exact-size - put as much packets as possible in one frame, until the framer-limit limit is met, even if fragmentation will be needed (best performance)
dynamic-size - choose the best frame size dynamically
Notes
Such settings as enable-polling, framer-policy and framer-limit are relevant only on Access Point, they are ignored for client devices! The client automatically adapts to AP settings.
WDS for Nstreme protocol requires using station-wds mode on one of the peers. Configurations with WDS between AP modes (bridge and ap-bridge) will not work.
Example
To enable the nstreme protocol on the wlan1 radio with exact-size framing:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless nstreme> print
0 name="wlan1" enable-nstreme=no enable-polling=yes framer-policy=none
framer-limit=3200
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless nstreme> set wlan1 enable-nstreme=yes \
\... framer-policy=exact-size
Nstreme2 Group Settings
Submenu level: /interface wireless nstreme-dualDescription
Two radios in nstreme-dual-slave mode can be grouped together to make nstreme2 Point-to-Point connection. To put wireless interfaces into a nstreme2 group, you should set their mode to nstreme-dual-slave. Many parameters from /interface wireless menu are ignored, using the nstreme2, except:
- frequency-mode
- country
- antenna-gain
- tx-power
- tx-power-mode
- antenna-mode
Property Description
arp (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only; default: enabled) - Address Resolution Protocol settingdisable-running-check (yes | no) - whether the interface should always be treated as running even if there is no connection to a remote peerframer-limit (integer; default: 2560) - maximal frame sizeframer-policy (none | best-fit | exact-size; default: none) - the method how to combine frames (like fast-frames setting in interface configuration). A number of frames may be combined into one bigger one to reduce the amout of protocol overhead (and thus increase speed). The card are not waiting for frames, but in case a number packets are queued for transmitting, they can be combined. There are several methods of framing:best-fit - put as much packets as possible in one frame, until the framer-limit limit is met, but do not fragment packets
exact-size - put as much packets as possible in one frame, until the framer-limit limit is met, even if fragmentation will be needed (best performance)
2.4ghz-g - IEEE 802.11g
2.4ghz-g-turbo - IEEE 802.11g in Atheros proprietary turbo mode (up to 108Mbit)
5ghz - IEEE 802.11a up to 54 Mbit
5ghz-turbo - IEEE 802.11a in Atheros proprietary turbo mode (up to 108Mbit)
2.4ghz-g - IEEE 802.11g
2.4ghz-g-turbo - IEEE 802.11g in Atheros proprietary turbo mode (up to 108Mbit)
5ghz - IEEE 802.11a up to 54 Mbit
5ghz-turbo - IEEE 802.11a in Atheros proprietary turbo mode (up to 108Mbit)
Notes
WDS cannot be used on Nstreme-dual links.
The difference between tx-freq and rx-freq should be about 200MHz (more is recommended) because of the interference that may occur!
You can use different bands for rx and tx links. For example, transmit in 2.4ghz-g-turbo and receive data, using 2.4ghz-b band.
Example
To enable the nstreme2 protocol on a router:
-
Having two Atheros AR5212 based cards which are not used for anything else, to group them into a nstreme interface, switch both of them into nstreme-dual-slave mode:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:31:02:4F arp=enabled disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5212 radio-name="000B6B31024F" mode=station ssid="MikroTik" frequency=5180 band=5GHz scan-list=default-ism supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps, 54Mbps basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007 ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default noise-floor-threshold=default burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes hide-ssid=no 802.1x-mode=none 1 name="wlan2" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:30:B4:A4 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5212 radio-name="000B6B30B4A4" mode=station ssid="MikroTik" frequency=5180 band=5GHz scan-list=default-ism supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps, 54Mbps basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007 ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default noise-floor-threshold=default burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes hide-ssid=no 802.1x-mode=none [admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> set 0,1 mode=nstreme-dual-slave -
Then add nstreme2 interface with exact-size framing:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless nstreme-dual> add \ \... framer-policy=exact-size -
Configure which card will be receiving and which - transmitting and specify remote receiver card's MAC address:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless nstreme-dual> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 X name="n-streme1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no tx-radio=(unknown) rx-radio=(unknown) remote-mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 tx-band=5GHz tx-frequency=5180 rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,54Mbps rx-band=5GHz rx-frequency=5320 framer-policy=exact-size framer-limit=4000 [admin@MikroTik] interface wireless nstreme-dual> set 0 disabled=no \ \... tx-radio=wlan1 rx-radio=wlan2 remote-mac=00:0C:42:05:0B:12 [admin@MikroTik] interface wireless nstreme-dual> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 X name="n-streme1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:30:B4:A4 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no tx-radio=wlan1 rx-radio=wlan2 remote-mac=00:0C:42:05:0B:12 tx-band=5GHz tx-frequency=5180 rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,54Mbps rx-band=5GHz rx-frequency=5320 framer-policy=exact-size framer-limit=4000
Registration Table
Submenu level: /interface wireless registration-tableDescription
In the registration table you can see various information about currently connected clients. It is used only for Access Points.
Property Description
ap (read-only: no | yes) - whether the connected device is an Access Point or notbytes (read-only: integer, integer) - number of sent and received packet bytesframe-bytes (read-only: integer, integer) - number of sent and received data bytes excluding header informationframes (read-only: integer, integer) - number of sent and received 802.11 data frames excluding retransmitted data framesframing-current-size (read-only: integer) - current size of combined framesframing-limit (read-only: integer) - maximal size of combined framesframing-mode (read-only: none | best-fit | exact-size; default: none) - the method how to combine frameshw-frame-bytes (read-only: integer, integer) - number of sent and received data bytes including header informationhw-frames (read-only: integer, integer) - number of sent and received 802.11 data frames including retransmitted data framesinterface (read-only: name) - interface that client is registered tolast-activity (read-only: time) - last interface data tx/rx activitylast-ip (read-only: IP address) - IP address found in the last IP packet received from the registered clientmac-address (read-only: MAC address) - MAC address of the registered clientpackets (read-only: integer, integer) - number of sent and received network layer packetspacking-size (read-only: integer) - maximum packet size in bytesparent (read-only: MAC address) - parent access point's MAC address, if forwarded from another access pointrouteros-version (read-only: name) - RouterOS version of the registered clientrx-ccq (read-only: integer: 0..100) - Client Connection Quality - a value in percent that shows how effective the receive bandwidth is used regarding the theoretically maximum available bandwidth. Mostly it depends from an amount of retransmited wireless frames.rx-packed (read-only: integer) - number of received packets in form of received-packets/number of packets, which were packed into a larger ones, using fast-framesrx-rate (read-only: integer) - receive data ratesignal-strength (read-only: integer) - average strength of the client signal recevied by the APtx-ccq (read-only: integer: 0..100) - Client Connection Quality - a value in percent that shows how effective the transmit bandwidth is used regarding the theoretically maximum available bandwidth. Mostly it depends from an amount of retransmited wireless frames.tx-packed (read-only: integer) - number of sent packets in form of sent-packets/number of packets, which were packed into a larger ones, using fast-framestx-rate (read-only: integer) - transmit data ratetx-signal-strength (read-only: integer) - average power of the AP transmit signal as received by the client devicetype (read-only: name) - type of the clientuptime (read-only: time) - time the client is associated with the access pointwds (read-only: no | yes) - whether the connected client is using wds or notExample
To see registration table showing all clients currently associated with the access point:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless registration-table> print # INTERFACE RADIO-NAME MAC-ADDRESS AP SIGNAL... TX-RATE 0 wireless1 000124705304 00:01:24:70:53:04 no -38dBm... 9Mbps [admin@MikroTik] interface wireless registration-table>
To get additional statistics:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> registration-table print stats
0 interface=dfaewad radio-name="000C42050436" mac-address=00:0C:42:05:04:36
ap=yes wds=no rx-rate=54Mbps tx-rate=54Mbps packets=597,668
bytes=48693,44191 frames=597,673 frame-bytes=48693,44266 hw-frames=597,683
hw-frame-bytes=63021,60698 uptime=45m28s last-activity=0s
signal-strength=-66dBm@54Mbps
strength-at-rates=-59dBm@1Mbps 13s120ms,-61dBm@6Mbps 7s770ms,-61dBm@9Mbps
40m43s970ms,-60dBm@12Mbps 40m43s760ms,-61dBm@18Mbps
40m43s330ms,-60dBm@24Mbps 40m43s,-61dBm@36Mbps
33m10s230ms,-62dBm@48Mbps 33m9s760ms,-66dBm@54Mbps 10ms
tx-signal-strength=-65dBm tx-ccq=24% rx-ccq=20% ack-timeout=28 distance=28
nstreme=no framing-mode=none routeros-version="2.9rc5"
last-ip=192.168.63.8
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless>
Connect List
Submenu level: /interface wireless connect-listDescription
The Connect List is a list of rules (order is important), that determine to which AP the station should connect to.
At first, the station is searching for APs all frequencies (from scan-list) in the respective band and makes a list of Access Points. If the ssid is set under /interface wireless, the router removes all Access Points from its AP list which do not have such ssid
If a rule is matched and the parameter connect is set to yes, the station will connect to this AP. If the parameter says connect=no or the rule is not matched, we jump to the next rule.
If we have gone through all rules and haven't connected to any AP, yet. The router chooses an AP with the best signal and ssid that is set under /interface wireless.
In case when the station has not connected to any AP, this process repeats from beginning.
Property Description
area-prefix (text) - a string that indicates the beginning from the area string of the AP. If the AP's area begins with area-prefix, then this parameter returns trueconnect (yes | no) - whether to connect to AP that matches this ruleinterface (name) - name of the wireless interfacemac-address (MAC address) - MAC address of the AP. If set to 00:00:00:00:00:00, all APs are acceptedmin-signal-strength (integer) - signal strength in dBm. Rule is matched, if the signal from AP is stronger than thissecurity-profile (name; default: none) - name of the security profile, used to connect to the AP. If none, then those security profile is used which is configured for the respective interfacessid (text) - the ssid of the AP. If none set, all ssid's are accepted. Different ssids will be meaningful, if the ssid for the respective interface is set to ""Access List
Submenu level: /interface wireless access-listDescription
The access list is used by the Access Point to restrict associations of clients. This list contains MAC addresses of clients and determines what action to take when client attempts to connect. Also, the forwarding of frames sent by the client is controlled.
The association procedure is as follows: when a new client wants to associate to the AP that is configured on interface wlanN, an entry with client's MAC address and interface wlanN is looked up in the access-list. If such entry is found, action specified in the access list is performed, else default-authentication and default-forwarding arguments of interface wlanN are taken.
Property Description
ap-tx-limit (integer; default: 0) - limits data rate for this wireless client (in bps)Notes
If you have default authentication action for the interface set to yes, you can disallow this node to register at the AP's interface wlanN by setting authentication=no for it. Thus, all nodes except this one will be able to register to the interface wlanN.
If you have default authentication action for the interface set to no, you can allow this node to register at the AP's interface wlanN by setting authentication=yes for it. Thus, only the specified nodes will be able to register to the interface wlanN.
Example
To allow authentication and forwarding for the client 00:01:24:70:3A:BB from the wlan1 interface using WEP 40bit algorithm with the key 1234567890:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless access-list> add mac-address= \
\... 00:01:24:70:3A:BB interface=wlan1 private-algo=40bit-wep private-key=1234567890
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless access-list> print
Flags: X - disabled
0 mac-address=00:01:24:70:3A:BB interface=wlan1 authentication=yes
forwarding=yes ap-tx-limit=0 client-tx-limit=0 private-algo=40bit-wep
private-key="1234567890"
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless access-list>
Info
Submenu level: /interface wireless infoDescription
This facility provides you with general wireless interface information.
Property Description
2ghz-b-channels (multiple choice, read-only: 2312, 2317, 2322, 2327, 2332, 2337, 2342, 2347, 2352, 2357, 2362, 2367, 2372, 2412, 2417, 2422, 2427, 2432, 2437, 2442, 2447, 2452, 2457, 2462, 2467, 2472, 2484, 2512, 2532, 2552, 2572, 2592, 2612, 2632, 2652, 2672, 2692, 2712, 2732) - the list of 2GHz IEEE 802.11b channels (frequencies are given in MHz)2ghz-g-channels (multiple choice, read-only: 2312, 2317, 2322, 2327, 2332, 2337, 2342, 2347, 2352, 2357, 2362, 2367, 2372, 2412, 2417, 2422, 2427, 2432, 2437, 2442, 2447, 2452, 2457, 2462, 2467, 2472, 2512, 2532, 2552, 2572, 2592, 2612, 2632, 2652, 2672, 2692, 2712, 2732, 2484) - the list of 2GHz IEEE 802.11g channels (frequencies are given in MHz)5ghz-channels (multiple choice, read-only: 4920, 4925, 4930, 4935, 4940, 4945, 4950, 4955, 4960, 4965, 4970, 4975, 4980, 4985, 4990, 4995, 5000, 5005, 5010, 5015, 5020, 5025, 5030, 5035, 5040, 5045, 5050, 5055, 5060, 5065, 5070, 5075, 5080, 5085, 5090, 5095, 5100, 5105, 5110, 5115, 5120, 5125, 5130, 5135, 5140, 5145, 5150, 5155, 5160, 5165, 5170, 5175, 5180, 5185, 5190, 5195, 5200, 5205, 5210, 5215, 5220, 5225, 5230, 5235, 5240, 5245, 5250, 5255, 5260, 5265, 5270, 5275, 5280, 5285, 5290, 5295, 5300, 5305, 5310, 5315, 5320, 5325, 5330, 5335, 5340, 5345, 5350, 5355, 5360, 5365, 5370, 5375, 5380, 5385, 5390, 5395, 5400, 5405, 5410, 5415, 5420, 5425, 5430, 5435, 5440, 5445, 5450, 5455, 5460, 5465, 5470, 5475, 5480, 5485, 5490, 5495, 5500, 5505, 5510, 5515, 5520, 5525, 5530, 5535, 5540, 5545, 5550, 5555, 5560, 5565, 5570, 5575, 5580, 5585, 5590, 5595, 5600, 5605, 5610, 5615, 5620, 5625, 5630, 5635, 5640, 5645, 5650, 5655, 5660, 5665, 5670, 5675, 5680, 5685, 5690, 5695, 5700, 5705, 5710, 5715, 5720, 5725, 5730, 5735, 5740, 5745, 5750, 5755, 5760, 5765, 5770, 5775, 5780, 5785, 5790, 5795, 5800, 5805, 5810, 5815, 5820, 5825, 5830, 5835, 5840, 5845, 5850, 5855, 5860, 5865, 5870, 5875, 5880, 5885, 5890, 5895, 5900, 5905, 5910, 5915, 5920, 5925, 5930, 5935, 5940, 5945, 5950, 5955, 5960, 5965, 5970, 5975, 5980, 5985, 5990, 5995, 6000, 6005, 6010, 6015, 6020, 6025, 6030, 6035, 6040, 6045, 6050, 6055, 6060, 6065, 6070, 6075, 6080, 6085, 6090, 6095, 6100) - the list of 5GHz channels (frequencies are given in MHz)5ghz-turbo-channels (multiple choice, read-only: 4920, 4925, 4930, 4935, 4940, 4945, 4950, 4955, 4960, 4965, 4970, 4975, 4980, 4985, 4990, 4995, 5000, 5005, 5010, 5015, 5020, 5025, 5030, 5035, 5040, 5045, 5050, 5055, 5060, 5065, 5070, 5075, 5080, 5085, 5090, 5095, 5100, 5105, 5110, 5115, 5120, 5125, 5130, 5135, 5140, 5145, 5150, 5155, 5160, 5165, 5170, 5175, 5180, 5185, 5190, 5195, 5200, 5205, 5210, 5215, 5220, 5225, 5230, 5235, 5240, 5245, 5250, 5255, 5260, 5265, 5270, 5275, 5280, 5285, 5290, 5295, 5300, 5305, 5310, 5315, 5320, 5325, 5330, 5335, 5340, 5345, 5350, 5355, 5360, 5365, 5370, 5375, 5380, 5385, 5390, 5395, 5400, 5405, 5410, 5415, 5420, 5425, 5430, 5435, 5440, 5445, 5450, 5455, 5460, 5465, 5470, 5475, 5480, 5485, 5490, 5495, 5500, 5505, 5510, 5515, 5520, 5525, 5530, 5535, 5540, 5545, 5550, 5555, 5560, 5565, 5570, 5575, 5580, 5585, 5590, 5595, 5600, 5605, 5610, 5615, 5620, 5625, 5630, 5635, 5640, 5645, 5650, 5655, 5660, 5665, 5670, 5675, 5680, 5685, 5690, 5695, 5700, 5705, 5710, 5715, 5720, 5725, 5730, 5735, 5740, 5745, 5750, 5755, 5760, 5765, 5770, 5775, 5780, 5785, 5790, 5795, 5800, 5805, 5810, 5815, 5820, 5825, 5830, 5835, 5840, 5845, 5850, 5855, 5860, 5865, 5870, 5875, 5880, 5885, 5890, 5895, 5900, 5905, 5910, 5915, 5920, 5925, 5930, 5935, 5940, 5945, 5950, 5955, 5960, 5965, 5970, 5975, 5980, 5985, 5990, 5995, 6000, 6005, 6010, 6015, 6020, 6025, 6030, 6035, 6040, 6045, 6050, 6055, 6060, 6065, 6070, 6075, 6080, 6085, 6090, 6095, 6100) - the list of 5GHz-turbo channels (frequencies are given in MHz)ack-timeout-control (read-only: yes | no) - provides information whether this device supports transmission acceptance timeout controlalignment-mode (read-only: yes | no) - is the alignment-only mode supported by this interfaceburst-support (yes | no) - whether the interface supports data bursts (burst-time)chip-info (read-only: text) - information from EEPROMdefault-periodic-calibration (read-only: yes | no) - whether the card supports periodic-calibrationfirmware (read-only: text) - current firmware of the interface (used only for Prism chipset based cards)interface-type (read-only: text) - shows the hardware interface typenoise-floor-control (read-only: yes | no) - does this interface support noise-floor-thershold detectionnstreme-support (read-only: yes | no) - whether the card supports n-streme protocolscan-support (yes | no) - whether the interface supports scan function ('/interface wireless scan')supported-bands (multiple choice, read-only: 2ghz-b, 5ghz, 5ghz-turbo, 2ghz-g) - the list of supported bandstx-power-control (read-only: yes | no) - provides information whether this device supports transmission power controlvirtual-aps (read-only: yes | no) - whether this interface supports Virtual Access Points ('/interface wireless add')Notes
There is a special argument for the print command - print count-only. It forces the print command to print only the count of information topics.
/interface wireless info print command shows only channels supported by a particular card.
Example
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless info> print
0 interface-type=Atheros AR5413
chip-info="mac:0xa/0x5, phy:0x61, a5:0x63, a2:0x0, eeprom:0x5002"
tx-power-control=yes ack-timeout-control=yes alignment-mode=yes
virtual-aps=yes noise-floor-control=yes scan-support=yes burst-support=yes
nstreme-support=yes default-periodic-calibration=enabled
supported-bands=2ghz-b,5ghz,5ghz-turbo,2ghz-g,2ghz-g-turbo
2ghz-b-channels=2312:0,2317:0,2322:0,2327:0,2332:0,2337:0,2342:0,2347:0,
2352:0,2357:0,2362:0,2367:0,2372:0,2377:0,2382:0,2387:0,
2392:0,2397:0,2402:0,2407:0,2412:0,2417:0,2422:0,2427:0,
2432:0,2437:0,2442:0,2447:0,2452:0,2457:0,2462:0,2467:0,
2472:0,2477:0,2482:0,2487:0,2492:0,2497:0,2314:0,2319:0,
2324:0,2329:0,2334:0,2339:0,2344:0,2349:0,2354:0,2359:0,
2364:0,2369:0,2374:0,2379:0,2384:0,2389:0,2394:0,2399:0,
2404:0,2409:0,2414:0,2419:0,2424:0,2429:0,2434:0,2439:0,
2444:0,2449:0,2454:0,2459:0,2464:0,2469:0,2474:0,2479:0,
2484:0,2489:0,2494:0,2499:0
5ghz-channels=4920:0,4925:0,4930:0,4935:0,4940:0,4945:0,4950:0,4955:0,
4960:0,4965:0,4970:0,4975:0,4980:0,4985:0,4990:0,4995:0,
5000:0,5005:0,5010:0,5015:0,5020:0,5025:0,5030:0,5035:0,
5040:0,5045:0,5050:0,5055:0,5060:0,5065:0,5070:0,5075:0,
5080:0,5085:0,5090:0,5095:0,5100:0,5105:0,5110:0,5115:0,
5120:0,5125:0,5130:0,5135:0,5140:0,5145:0,5150:0,5155:0,
5160:0,5165:0,5170:0,5175:0,5180:0,5185:0,5190:0,5195:0,
5200:0,5205:0,5210:0,5215:0,5220:0,5225:0,5230:0,5235:0,
5240:0,5245:0,5250:0,5255:0,5260:0,5265:0,5270:0,5275:0,
5280:0,5285:0,5290:0,5295:0,5300:0,5305:0,5310:0,5315:0,
5320:0,5325:0,5330:0,5335:0,5340:0,5345:0,5350:0,5355:0,
5360:0,5365:0,5370:0,5375:0,5380:0,5385:0,5390:0,5395:0,
5400:0,5405:0,5410:0,5415:0,5420:0,5425:0,5430:0,5435:0,
5440:0,5445:0,5450:0,5455:0,5460:0,5465:0,5470:0,5475:0,
5480:0,5485:0,5490:0,5495:0,5500:0,5505:0,5510:0,5515:0,
5520:0,5525:0,5530:0,5535:0,5540:0,5545:0,5550:0,5555:0,
5560:0,5565:0,5570:0,5575:0,5580:0,5585:0,5590:0,5595:0,
5600:0,5605:0,5610:0,5615:0,5620:0,5625:0,5630:0,5635:0,
5640:0,5645:0,5650:0,5655:0,5660:0,5665:0,5670:0,5675:0,
5680:0,5685:0,5690:0,5695:0,5700:0,5705:0,5710:0,5715:0,
5720:0,5725:0,5730:0,5735:0,5740:0,5745:0,5750:0,5755:0,
5760:0,5765:0,5770:0,5775:0,5780:0,5785:0,5790:0,5795:0,
5800:0,5805:0,5810:0,5815:0,5820:0,5825:0,5830:0,5835:0,
5840:0,5845:0,5850:0,5855:0,5860:0,5865:0,5870:0,5875:0,
5880:0,5885:0,5890:0,5895:0,5900:0,5905:0,5910:0,5915:0,
5920:0,5925:0,5930:0,5935:0,5940:0,5945:0,5950:0,5955:0,
5960:0,5965:0,5970:0,5975:0,5980:0,5985:0,5990:0,5995:0,
6000:0,6005:0,6010:0,6015:0,6020:0,6025:0,6030:0,6035:0,
6040:0,6045:0,6050:0,6055:0,6060:0,6065:0,6070:0,6075:0,
6080:0,6085:0,6090:0,6095:0,6100:0
5ghz-turbo-channels=4920:0,4925:0,4930:0,4935:0,4940:0,4945:0,4950:0,4955:0,
4960:0,4965:0,4970:0,4975:0,4980:0,4985:0,4990:0,4995:0,
5000:0,5005:0,5010:0,5015:0,5020:0,5025:0,5030:0,5035:0,
5040:0,5045:0,5050:0,5055:0,5060:0,5065:0,5070:0,5075:0,
5080:0,5085:0,5090:0,5095:0,5100:0,5105:0,5110:0,5115:0,
5120:0,5125:0,5130:0,5135:0,5140:0,5145:0,5150:0,5155:0,
5160:0,5165:0,5170:0,5175:0,5180:0,5185:0,5190:0,5195:0,
5200:0,5205:0,5210:0,5215:0,5220:0,5225:0,5230:0,5235:0,
5240:0,5245:0,5250:0,5255:0,5260:0,5265:0,5270:0,5275:0,
5280:0,5285:0,5290:0,5295:0,5300:0,5305:0,5310:0,5315:0,
5320:0,5325:0,5330:0,5335:0,5340:0,5345:0,5350:0,5355:0,
5360:0,5365:0,5370:0,5375:0,5380:0,5385:0,5390:0,5395:0,
5400:0,5405:0,5410:0,5415:0,5420:0,5425:0,5430:0,5435:0,
5440:0,5445:0,5450:0,5455:0,5460:0,5465:0,5470:0,5475:0,
5480:0,5485:0,5490:0,5495:0,5500:0,5505:0,5510:0,5515:0,
5520:0,5525:0,5530:0,5535:0,5540:0,5545:0,5550:0,5555:0,
5560:0,5565:0,5570:0,5575:0,5580:0,5585:0,5590:0,5595:0,
5600:0,5605:0,5610:0,5615:0,5620:0,5625:0,5630:0,5635:0,
5640:0,5645:0,5650:0,5655:0,5660:0,5665:0,5670:0,5675:0,
5680:0,5685:0,5690:0,5695:0,5700:0,5705:0,5710:0,5715:0,
5720:0,5725:0,5730:0,5735:0,5740:0,5745:0,5750:0,5755:0,
5760:0,5765:0,5770:0,5775:0,5780:0,5785:0,5790:0,5795:0,
5800:0,5805:0,5810:0,5815:0,5820:0,5825:0,5830:0,5835:0,
5840:0,5845:0,5850:0,5855:0,5860:0,5865:0,5870:0,5875:0,
5880:0,5885:0,5890:0,5895:0,5900:0,5905:0,5910:0,5915:0,
5920:0,5925:0,5930:0,5935:0,5940:0,5945:0,5950:0,5955:0,
5960:0,5965:0,5970:0,5975:0,5980:0,5985:0,5990:0,5995:0,
6000:0,6005:0,6010:0,6015:0,6020:0,6025:0,6030:0,6035:0,
6040:0,6045:0,6050:0,6055:0,6060:0,6065:0,6070:0,6075:0,
6080:0,6085:0,6090:0,6095:0,6100:0
2ghz-g-channels=2312:0,2317:0,2322:0,2327:0,2332:0,2337:0,2342:0,2347:0,
2352:0,2357:0,2362:0,2367:0,2372:0,2377:0,2382:0,2387:0,
2392:0,2397:0,2402:0,2407:0,2412:0,2417:0,2422:0,2427:0,
2432:0,2437:0,2442:0,2447:0,2452:0,2457:0,2462:0,2467:0,
2472:0,2477:0,2482:0,2487:0,2492:0,2497:0,2314:0,2319:0,
2324:0,2329:0,2334:0,2339:0,2344:0,2349:0,2354:0,2359:0,
2364:0,2369:0,2374:0,2379:0,2384:0,2389:0,2394:0,2399:0,
2404:0,2409:0,2414:0,2419:0,2424:0,2429:0,2434:0,2439:0,
2444:0,2449:0,2454:0,2459:0,2464:0,2469:0,2474:0,2479:0,
2484:0,2489:0,2494:0,2499:0
2ghz-g-turbo-channels=2312:0,2317:0,2322:0,2327:0,2332:0,2337:0,2342:0,
2347:0,2352:0,2357:0,2362:0,2367:0,2372:0,2377:0,
2382:0,2387:0,2392:0,2397:0,2402:0,2407:0,2412:0,
2417:0,2422:0,2427:0,2432:0,2437:0,2442:0,2447:0,
2452:0,2457:0,2462:0,2467:0,2472:0,2477:0,2482:0,
2487:0,2492:0,2497:0,2314:0,2319:0,2324:0,2329:0,
2334:0,2339:0,2344:0,2349:0,2354:0,2359:0,2364:0,
2369:0,2374:0,2379:0,2384:0,2389:0,2394:0,2399:0,
2404:0,2409:0,2414:0,2419:0,2424:0,2429:0,2434:0,
2439:0,2444:0,2449:0,2454:0,2459:0,2464:0,2469:0,
2474:0,2479:0,2484:0,2489:0,2494:0,2499:0
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless>
Virtual Access Point Interface
Submenu level: /interface wirelessDescription
Virtual Access Point (VAP) interface is used to have an additional AP. You can create a new AP with different ssid and mac-address. It can be compared with a VLAN where the ssid from VAP is the VLAN tag and the hardware interface is the VLAN switch.
You can add up to 128 VAP interfaces for each hardware interface.
RouterOS supports VAP feature for Atheros AR5212 and newer.
Property Description
arp (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only) - ARP modedefault-authentication (yes | no; default: yes) - whether to accept or reject a client that wants to associate, but is not in the access-listdefault-forwarding (yes | no; default: yes) - whether to forward frames to other AP clients or notdisabled (yes | no; default: yes) - whether to disable the interface or notdisable-running-check (yes | no; default: no) - disable running check. For 'broken' cards it is a good idea to set this value to 'yes'hide-ssid (yes | no; default: no) - whether to hide ssid or not in the beacon frames:no - ssid is included in beacon frames. AP replies to probe-requests with the given ssid and to 'broadcast ssid'
Notes
The VAP MAC address is set by default to the same address as the physical interface has, with the second bit of the first byte set (i.e., the MAC address would start with 02). If that address is already used by some other wireless or VAP interface, it is increased by 1 until a free spot is found. When manually assigning MAC address, keep in mind that it should have the first bit of the first byte unset (so it should not be like 01, or A3). Note also that it is recommended to keep the MAC adress of VAP as similar (in terms of bit values) to the MAC address of the physical interface it is put onto, as possible, because the more different the addresses are, the more it affects performance.
WDS Interface Configuration
Submenu level: /interface wireless wdsDescription
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) allows packets to pass from one wireless AP (Access Point) to another, just as if the APs were ports on a wired Ethernet switch. APs must use the same standard (802.11a, 802.11b or 802.11g) and work on the same frequencies in order to connect to each other.
There are two possibilities to create a WDS interface:
- dynamic - is created 'on the fly' and appers under wds menu as a dynamic interface
- static - is created manually
Property Description
arp (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only; default: enabled) - Address Resolution Protocolenabled - the interface will use ARP
proxy-arp - the interface will use the ARP proxy feature
reply-only - the interface will only reply to the requests originated to its own IP addresses. Neighbour MAC addresses will be resolved using /ip arp statically set table only
Notes
When the link between WDS devices, using wds-mode=dynamic, goes down, the dynamic WDS interfaces disappear and if there are any IP addresses set on this interface, their 'interface' setting will change to (unknown). When the link comes up again, the 'interface' value will not change - it will remain as (unknown). That's why it is not recommended to add IP addresses to dynamic WDS interfaces.
If you want to use dynamic WDS in a bridge, set the wds-default-bridge value to desired bridge interface name. When the link will go down and then it comes up, the dynamic WDS interface will be put in the specified bridge automatically.
As the routers which are in WDS mode have to communicate at equal frequencies, it is not recommended to use WDS and DFS simultaneously - it is most probable that these routers will not connect to each other.
WDS significantly faster than EoIP (up to 10-20% on RouterBOARD 500 systems), so it is recommended to use WDS whenever possible.
Example
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless wds> add master-interface=wlan1 \
\... wds-address=00:0B:6B:30:2B:27 disabled=no
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless wds> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running, D - dynamic
0 R name="wds1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:30:2B:23 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no master-inteface=wlan1
wds-address=00:0B:6B:30:2B:27
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless wds>
Align
Submenu level: /interface wireless alignDescription
This feature is created to position wireless links. The align submenu describes properties which are used if /interface wireless mode is set to alignment-only. In this mode the interface 'listens' to those packets which are sent to it from other devices working on the same channel. The interface also can send special packets which contains information about its parameters.
Property Description
active-mode (yes | no; default: yes) - whether the interface will receive and transmit 'alignment' packets or it will only receive themaudio-max (integer; default: -20) - signal-strength at which audio (beeper) frequency will be the highestaudio-min (integer; default: -100) - signal-strength at which audio (beeper) frequency will be the lowestaudio-monitor (MAC address; default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) - MAC address of the remote host which will be 'listened'filter-mac (MAC address; default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) - in case if you want to receive packets from only one remote host, you should specify here its MAC addressframe-size (integer: 200..1500; default: 300) - size of 'alignment' packets that will be transmittedframes-per-second (integer: 1..100; default: 25) - number of frames that will be sent per second (in active-mode)receive-all (yes | no; default: no) - whether the interface gathers packets about other 802.11 standard packets or it will gather only 'alignment' packetsssid-all (yes | no; default: no) - whether you want to accept packets from hosts with other ssid than yourstest-audio (integer) - test the beeper for 10 secondsNotes
If you are using the command /interface wireless align monitor then it will automatically change the wireless interface's mode from station, bridge or ap-bridge to alignment-only.
Example
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless align> print
frame-size: 300
active-mode: yes
receive-all: yes
audio-monitor: 00:00:00:00:00:00
filter-mac: 00:00:00:00:00:00
ssid-all: no
frames-per-second: 25
audio-min: -100
audio-max: -20
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless align>
Align Monitor
Command name: /interface wireless align monitorDescription
This command is used to monitor current signal parameters to/from a remote host.
Property Description
address (read-only: MAC address) - MAC address of the remote hostavg-rxq (read-only: integer) - average signal strength of received packets since last display update on screencorrect (read-only: percentage) - how many undamaged packets were receivedlast-rx (read-only: time) - time in seconds before the last packet was receivedlast-tx (read-only: time) - time in seconds when the last TXQ info was receivedrxq (read-only: integer) - signal strength of last received packetssid (read-only: text) - service set identifiertxq (read-only: integer) - the last received signal strength from our host to the remote oneExample
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless align> monitor wlan2 # ADDRESS SSID RXQ AVG-RXQ LAST-RX TXQ LAST-TX CORRECT 0 00:01:24:70:4B:FC wirelesa -60 -60 0.01 -67 0.01 100 % [admin@MikroTik] interface wireless align>
Frequency Monitor
Description
Aproximately shows how loaded are the wireless channels.
Property Description
freq (read-only: integer) - shows current channeluse (read-only: percentage) - shows usage in current channelExample
Monitor 802.11b network load:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> frequency-monitor wlan1 FREQ USE 2412MHz 3.8% 2417MHz 9.8% 2422MHz 2% 2427MHz 0.8% 2432MHz 0% 2437MHz 0.9% 2442MHz 0.9% 2447MHz 2.4% 2452MHz 3.9% 2457MHz 7.5% 2462MHz 0.9%
To monitor other bands, change the the band setting for the respective wireless interface.
Manual Transmit Power Table
Submenu level: /interface wireless manual-tx-power-tableDescription
In this submenu you can define signal strength for each rate. You should be aware that you can damage your wireless card if you set higher output power than it is allowed. Note that the values in this table are set in dBm! NOT in mW! Therefore this table is used mainly to reduce the transmit power of the card.
Property Description
manual-tx-powers (text) - define tx-power in dBm for each rate, separate by commasExample
To set the following transmit powers at each rates: 1Mbps@10dBm, 2Mbps@10dBm, 5.5Mbps@9dBm, 11Mbps@7dBm, do the following:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless manual-tx-power-table> print
0 name="wlan1" manual-tx-powers=1Mbps:17,2Mbps:17,5.5Mbps:17,11Mbps:17,6Mbps:17
,
9Mbps:17,12Mbps:17,18Mbps:17,24Mbps:17,
36Mbps:17,48Mbps:17,54Mbps:17
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless manual-tx-power-table> set 0 \
manual-tx-powers=1Mbps:10,2Mbps:10,5.5Mbps:9,11Mbps:7
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless manual-tx-power-table> print
0 name="wlan1" manual-tx-powers=1Mbps:10,2Mbps:10,5.5Mbps:9,11Mbps:7
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless manual-tx-power-table>
Network Scan
Command name: /interface wireless scan interface_nameDescription
This is a feature that allows you to scan all avaliable wireless networks. While scanning, the card unregisters itself from the access point (in station mode), or unregisters all clients (in bridge or ap-bridge mode). Thus, network connections are lost while scanning.
Property Description
address (read-only: MAC address) - MAC address of the APband (read-only: text) - in which standard does the AP operatebss (read-only: yes | no) - basic service setfreeze-time-interval (time; default: 1s) - time in seconds to refresh the displayed datafreq (read-only: integer) - the frequency of APinterface_name (name) - the name of interface which will be used for scanning APsprivacy (read-only: yes | no) - whether all data is encrypted or notsignal-strength (read-only: integer) - signal strength in dBmssid (read-only: text) - service set identifier of the APExample
Scan the 5GHz band:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> scan wlan1
Flags: A - active, B - bss, P - privacy, R - routeros-network, N - nstreme
ADDRESS SSID BAND FREQ SIG RADIO-NAME
AB R 00:0C:42:05:00:28 test 5ghz 5180 -77 000C42050028
AB R 00:02:6F:20:34:82 aap1 5ghz 5180 -73 00026F203482
AB 00:0B:6B:30:80:0F www 5ghz 5180 -84
AB R 00:0B:6B:31:B6:D7 www 5ghz 5180 -81 000B6B31B6D7
AB R 00:0B:6B:33:1A:D5 R52_test_new 5ghz 5180 -79 000B6B331AD5
AB R 00:0B:6B:33:0D:EA short5 5ghz 5180 -70 000B6B330DEA
AB R 00:0B:6B:31:52:69 MikroTik 5ghz 5220 -69 000B6B315269
AB R 00:0B:6B:33:12:BF long2 5ghz 5260 -55 000B6B3312BF
-- [Q quit|D dump|C-z pause]
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless>
Security Profiles
Submenu level: /interface wireless security-profilesDescription
This section provides WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and WPA/WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) functions to wireless interfaces.
WPAThe Wi-Fi Protected Access is a combination of 802.1X, EAP, MIC, TKIP and AES. This is a easy to configure and secure wireless mechanism. It has been later updated to version 2, to provide greater security.
WEPThe Wired Equivalent Privacy encrypts data only between 802.11 devices, using static keys. It is not considered a very secure wireless data encryption mechanism, though it is better than no encryption at all.
The configuration of WEP is quite simple, using MikroTik RouterOS security profiles.
Property Description
authentication-types (multiple choice: wpa-psk | wpa2-psk | wpa-eap | wpa2-eap; default: "") - the list of accepted authentication types. APs will advertise the listed types. Stations will choose the AP, which supports the "best" type from the list (WPA2 is always preferred to WPA1; EAP is preferred to PSK)eap-methods (multiple choice: eap-tls | passthrough) - the ordered list of EAP methods. APs will to propose to the stations one by one (if first method listed is rejected, the next one is tried). Stations will accept first proposed method that will be on the listpassthrough - relay the authentication process to the RADIUS server (not used by the stations)
aes-ccm - more secure WPA encryption protocol, based on the reliable AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). Networks free of WEP legacy should use only this
static-keys-optional - if there is a static-sta-private-key set, use it. Otherwise, if the interface is set in an AP mode, do not use encryption, if the the interface is in station mode, use encryption if the static-transmit-key is set
static-keys-required - encrypt all packets and accept only encrypted packets
dynamic-keys - generate encryptioon keys dynamically
40bit-wep - use the 40bit encryption (also known as 64bit-wep) and accept only these packets
104bit-wep - use the 104bit encryption (also known as 128bit-wep) and accept only these packets
aes-ccm - use the AES-CCM (Advanced Encryption Standard in Counter with CBC-MAC) encryption algorithm and accept only these packets
tkip - use the TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) and accept only these packets
40bit-wep - use the 40bit encryption (also known as 64bit-wep) and accept only these packets
104bit-wep - use the 104bit encryption (also known as 128bit-wep) and accept only these packets
aes-ccm - use the AES-CCM (Advanced Encryption Standard in Counter with CBC-MAC) encryption algorithm and accept only these packets
tkip - use the TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) and accept only these packets
40bit-wep - use the 40bit encryption (also known as 64bit-wep) and accept only these packets
104bit-wep - use the 104bit encryption (also known as 128bit-wep) and accept only these packets
aes-ccm - use the AES-CCM (Advanced Encryption Standard in Counter with CBC-MAC) encryption algorithm and accept only these packets
tkip - use the TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) and accept only these packets
40bit-wep - use the 40bit encryption (also known as 64bit-wep) and accept only these packets
104bit-wep - use the 104bit encryption (also known as 128bit-wep) and accept only these packets
aes-ccm - use the AES-CCM (Advanced Encryption Standard in Counter with CBC-MAC) encryption algorithm and accept only these packets
tkip - use the TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) and accept only these packets
dont-verify-certificate - require a certificate, but do not chack, if it has been signed by the available CA certificate
verify-certificate - require a certificate and verify that it has been signed by the available CA certificate
aes-ccm - more secure WPA encryption protocol, based on the reliable AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). Networks free of WEP legacy should use only this
Notes
The keys used for encryption are in hexadecimal form. If you use 40bit-wep, the key has to be 10 characters long, if you use 104bit-wep, the key has to be 26 characters long.
Prism card doesn't report that the use of WEP is required for all data type frames, which means that some clients will not see that access point uses encryption and will not be able to connect to such AP. This is a Prism hardware problem and can not be fixed. Use Atheros-based cards (instead of Prism) on APs if you want to provide WEP in your wireless network.
Wireless encryption cannot work together with wireless compression.
Sniffer
Submenu level: /interface wireless snifferDescription
With wireless sniffer you can sniff packets from wireless networks.
Property Description
channel-time (time; default: 200ms) - how long to sniff each channel, if multiple-channels is set to yesfile-limit (integer; default: 10) - limits file-name's file size (measured in kilobytes)file-name (text; default: "") - name of the file where to save packets in PCAP format. If file-name is not defined, packets are not saved into a filememory-limit (integer; default: 1000) - how much memory to use (in kilobytes) for sniffed packetsmultiple-channels (yes | no; default: no) - whether to sniff multiple channels or a single channelyes - sniff in all channels that are listed in the scan-list in /interface wireless
Sniffer Sniff
Submenu level: /interface wireless sniffer sniffDescription
Wireless Sniffer Sniffs packets
Property Description
file-over-limit-packets (read-only: integer) - how many packets are dropped because of exceeding file-limitfile-saved-packets (read-only: integer) - number of packets saved to filefile-size (read-only: integer) - current file size (kB)memory-over-limit-packets (read-only: integer) - number of packets that are dropped because of exceeding memory-limitmemory-saved-packets (read-only: integer) - how many packets are stored in mermorymemory-size (read-only: integer) - how much memory is currently used for sniffed packets (kB)processed-packets (read-only: integer) - number of sniffed packetsreal-file-limit (read-only: integer) - the real file size limit. It is calculated from the beginning of sniffing to reserve at least 1MB free space on the diskreal-memory-limit (read-only: integer) - the real memory size limit. It is calculated from the beginning of sniffing to reserve at least 1MB of free space in the memorystream-dropped-packets (read-only: integer) - number of packets that are dropped because of exceeding streaming-max-ratestream-sent-packets (read-only: integer) - number of packets that are sent to the streaming serverCommand Description
save - saves sniffed packets from the memory to file-name in PCAP formatSniffer Packets
Description
Wireless Sniffer sniffed packets. If packets Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) field detects error, it will be displayed by crc-error flag.
Property Description
dst (read-only: MAC address) - the receiver's MAC addressfreq (read-only: integer) - frequencyinterface (read-only: text) - wireless interface that captures packetssignal@rate (read-only: text) - at which signal-strength and rate was the packet receivedsrc (read-only: MAC address) - the sender's MAC addresstime (read-only: time) - time when the packet was received, starting from the beginning of sniffingtype (read-only: assoc-req | assoc-resp | reassoc-req | reassoc-resp | probe-req | probe-resp | beacon | atim | disassoc | auth | deauth | ps-poll | rts | cts | ack | cf-end | cf-endack | data | d-cfack | d-cfpoll | d-cfackpoll | data-null | nd-cfack | nd-cfpoll | nd-cfackpoll) - type of the sniffed packetExample
Sniffed packets:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless sniffer packet> pr Flags: E - crc-error # FREQ SIGNAL@RATE SRC DST TYPE 0 2412 -73dBm@1Mbps 00:0B:6B:31:00:53 FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF beacon 1 2412 -91dBm@1Mbps 00:02:6F:01:CE:2E FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF beacon 2 2412 -45dBm@1Mbps 00:02:6F:05:68:D3 FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF beacon 3 2412 -72dBm@1Mbps 00:60:B3:8C:98:3F FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF beacon 4 2412 -65dBm@1Mbps 00:01:24:70:3D:4E FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF probe-req 5 2412 -60dBm@1Mbps 00:01:24:70:3D:4E FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF probe-req 6 2412 -61dBm@1Mbps 00:01:24:70:3D:4E FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF probe-req
Snooper
Submenu level: /interface wireless snooperDescription
With wireless snooper you can monitor the traffic load on each channel.
Property Description
channel-time (time; default: 200ms) - how long to snoop each channel, if multiple-channels is set to yesmultiple-channels (yes | no; default: no) - whether to snoop multiple channels or a single channelyes - snoop in all channels that are listed in the scan-list in /interface wireless
Command Description
snoop - starts monitoring wireless channelsExample
Snoop 802.11b network:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless snooper> snoop wlan1 BAND FREQ USE BW NET-COUNT STA-COUNT 2.4ghz-b 2412MHz 1.5% 11.8kbps 2 2 2.4ghz-b 2417MHz 1.3% 6.83kbps 0 1 2.4ghz-b 2422MHz 0.6% 4.38kbps 1 1 2.4ghz-b 2427MHz 0.6% 4.43kbps 0 0 2.4ghz-b 2432MHz 0.3% 2.22kbps 0 0 2.4ghz-b 2437MHz 0% 0bps 0 0 2.4ghz-b 2442MHz 1% 8.1kbps 0 0 2.4ghz-b 2447MHz 1% 8.22kbps 1 1 2.4ghz-b 2452MHz 1% 8.3kbps 0 0 2.4ghz-b 2457MHz 0% 0bps 0 0 2.4ghz-b 2462MHz 0% 0bps 0 0 [admin@MikroTik] interface wireless snooper>
Application Examples
Station and AccessPoint
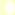
This example shows how to configure 2 MikroTik routers - one as Access Point and the other one as a station on 5GHz (802.11a standard).
-
On Access Point:
- mode=ap-bridge
- frequency=5805
- band=5ghz
- ssid=test
- disabled=no
On client (station):
- mode=station
- band=5ghz
- ssid=test
- disabled=no
-
Configure the Access Point and add an IP address (10.1.0.1) to it:
[admin@AccessPoint] interface wireless> set 0 mode=ap-bridge frequency=5805 \ band=5ghz disabled=no ssid=test name=AP [admin@AccessPoint] interface wireless> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 name="AP" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413 radio-name="000C42050022" mode=ap-bridge ssid="test" area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0 frequency=5805 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps, 54Mbps basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007 ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0 hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both [admin@AccessPoint] interface wireless> /ip add [admin@AccessPoint] ip address> add address=10.1.0.1/24 interface=AP [admin@AccessPoint] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 10.1.0.1/24 10.1.0.0 10.1.0.255 AP [admin@AccessPoint] ip address> -
Configure the station and add an IP address (10.1.0.2) to it:
[admin@Station] interface wireless> set wlan1 name=To-AP mode=station \ ssid=test band=5ghz disabled=no [admin@Station] interface wireless> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 R name="To-AP" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:34:5A:91 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5213 radio-name="000B6B345A91" mode=station ssid="test" area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0 frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps, 54Mbps basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007 ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0 hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both [admin@Station] interface wireless> /ip address [admin@Station] ip address> add address=10.1.0.2/24 interface=To-AP [admin@Station] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 172.16.0.2/24 172.16.0.0 172.16.0.255 To-AP 1 192.168.2.3/24 192.168.2.0 192.168.2.255 To-AP 2 10.1.0.2/24 10.1.0.0 10.1.0.255 To-AP [admin@Station] ip address> -
Check whether you can ping the Access Point from Station:
[admin@Station] > ping 10.1.0.1 10.1.0.1 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=3 ms 10.1.0.1 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=3 ms 10.1.0.1 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=3 ms 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 3/3.0/3 ms [admin@Station] >
WDS Station
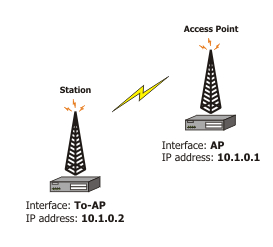
Using 802.11 set of standards you cannot simply bridge wireless stations. To solve this problem, the wds-station mode was created - it works just like a station, but connects only to APs that support WDS.
This example shows you how to make a transparent network, using the Station WDS feature:
On WDS Access Point:
- Configure AP to support WDS connections
- Set wds-default-bridge to bridge1
On WDS station:
- Configure it as a WDS Station, using mode=station-wds
Configure the WDS Access Point. Configure the wireless interface and put it into a bridge, and define that the dynamic WDS links should be automatically put into the same bridge:
[admin@WDS_AP] > interface bridge
[admin@WDS_AP] interface bridge> add
[admin@WDS_AP] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=B0:62:0D:08:FF:FF stp=no
priority=32768 ageing-time=5m forward-delay=15s
garbage-collection-interval=4s hello-time=2s max-message-age=20s
[admin@WDS_AP] interface bridge> port
[admin@WDS_AP] interface bridge port> print
# INTERFACE BRIDGE PRIORITY PATH-COST
0 Public none 128 10
1 wlan1 none 128 10
[admin@WDS_AP] interface bridge port> set 0 bridge=bridge1
[admin@WDS_AP] interface bridge port> /in wireless
[admin@WDS_AP] interface wireless> set wlan1 mode=ap-bridge ssid=wds-sta-test \
wds-mode=dynamic wds-default-bridge=bridge1 disabled=no band=2.4ghz-b/g \
frequency=2437
[admin@WDS_AP] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050022" mode=ap-bridge ssid="wds-sta-test" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=2437 band=2.4ghz-b/g scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=dynamic wds-default-bridge=bridge1 wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@WDS_AP] interface wireless>
Now configure the WDS station and put the wireless (wlan1) and ethernet (Local) interfaces into a bridge:
[admin@WDS_Station] > interface bridge
[admin@WDS_Station] interface bridge> add
[admin@WDS_Station] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=11:05:00:00:02:00 stp=no
priority=32768 ageing-time=5m forward-delay=15s
garbage-collection-interval=4s hello-time=2s max-message-age=20s
[admin@WDS_Station] interface bridge> port
[admin@WDS_Station] interface bridge port> print
# INTERFACE BRIDGE PRIORITY PATH-COST
0 Local none 128 10
1 wlan1 none 128 10
[admin@WDS_Station] interface bridge port> set 0,1 bridge=bridge1
[admin@WDS_Station] interface bridge port> /interface wireless
[admin@WDS_Station] interface wireless> set wlan1 mode=station-wds disabled=no \
\... ssid=wds-sta-test band=2.4ghz-b/g
[admin@WDS_Station] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:34:5A:91 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5213
radio-name="000B6B345A91" mode=station-wds ssid="wds-sta-test" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=2412 band=2.4ghz-b/g scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@WDS_Station] interface wireless>
Virtual Access Point
Virtual Access Point (VAP) enables you to create multiple Access Points with different Service Set Identifier, WDS settings, and even different MAC address, using the same hardware interface. You can create up to 7 VAP interfaces from a single physical interface. To create a Virtual Access Point, simply add a new interface, specifying a master-interface which is the physical interface that will do the hardware function to VAP.
This example will show you how to create a VAP:
[admin@VAP] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050022" mode=ap-bridge ssid="test" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=2437 band=2.4ghz-b/g scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@VAP] interface wireless> add master-interface=wlan1 ssid=virtual-test \
\... mac-address=00:0C:42:12:34:56 disabled=no name=V-AP
[admin@VAP] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050022" mode=ap-bridge ssid="test" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=2437 band=2.4ghz-b/g scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
1 name="V-AP" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:12:34:56 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=virtual-AP
master-interface=wlan1 ssid="virtual-test" area=""
max-station-count=2007 wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none
wds-ignore-ssid=no default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes
default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0 hide-ssid=no
security-profile=default
[admin@VAP] interface wireless>
When scanning from another router for an AP, you will see that you have 2 Access Points instead of one:
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> scan Station
Flags: A - active, B - bss, P - privacy, R - routeros-network, N - nstreme
ADDRESS SSID BAND FREQ SIG RADIO-NAME
AB R 00:0C:42:12:34:56 virtual-test 2.4ghz-g 2437 -72 000C42050022
AB R 00:0C:42:05:00:22 test 2.4ghz-g 2437 -72 000C42050022
-- [Q quit|D dump|C-z pause]
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless>
Note that the master-interface must be configured as an Access Point (ap-bridge or bridge mode)!
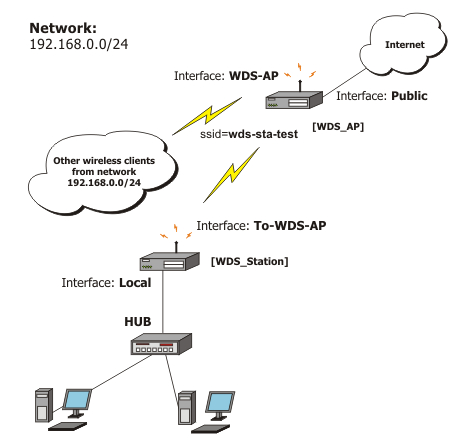
Nstreme
This example shows you how to configure a point-to-point Nstreme link.
The setup of Nstreme is similar to usual wireless configuration, except that you have to do some changes under /interface wireless nstreme.
-
Set the Nstreme-AP to bridge mode and enable Nstreme on it:
[admin@Nstreme-AP] interface wireless> set 0 mode=bridge ssid=nstreme \ \... band=5ghz frequency=5805 disabled=no [admin@Nstreme-AP] interface wireless> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413 radio-name="000C42050022" mode=bridge ssid="nstreme" area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0 frequency=5805 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps, 54Mbps basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007 ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0 hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both [admin@Nstreme-AP] interface wireless> nstreme [admin@Nstreme-AP] interface wireless nstreme> set wlan1 enable-nstreme=yes [admin@Nstreme-AP] interface wireless nstreme> print 0 name="wlan1" enable-nstreme=yes enable-polling=yes framer-policy=none framer-limit=3200 [admin@Nstreme-AP] interface wireless nstreme> -
Configure Nstreme-Client wireless settings and enable Nstreme on it:
[admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless> set wlan1 mode=station ssid=nstreme \ band=5ghz frequency=5805 disabled=no [admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:34:5A:91 arp=enabled disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5213 radio-name="000B6B345A91" mode=station ssid="nstreme" area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0 frequency=5805 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps, 54Mbps basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007 ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0 hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both [admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless> nstreme [admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless nstreme> set wlan1 enable-nstreme=yes [admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless nstreme> print 0 name="wlan1" enable-nstreme=yes enable-polling=yes framer-policy=none framer-limit=3200 [admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless nstreme>And monitor the link:
[admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless> monitor wlan1 status: connected-to-ess band: 5ghz frequency: 5805MHz tx-rate: 24Mbps rx-rate: 18Mbps ssid: "nstreme" bssid: 00:0C:42:05:00:22 radio-name: "000C42050022" signal-strength: -70dBm tx-signal-strength: -68dBm tx-ccq: 0% rx-ccq: 3% wds-link: no nstreme: yes polling: yes framing-mode: none routeros-version: "2.9rc2" current-tx-powers: 1Mbps:11,2Mbps:11,5.5Mbps:11,11Mbps:11,6Mbps:28, 9Mbps:28,12Mbps:28,18Mbps:28,24Mbps:28,36Mbps:25, 48Mbps:23,54Mbps:22 -- [Q quit|D dump|C-z pause] [admin@Nstreme-Client] interface wireless>
Dual Nstreme
The purpose of Nstreme2 (Dual Nstreme) is to make superfast point-to-point links, using 2 wireless cards on each router - one for receiving and the other one for transmitting data (you can use different bands for receiving and transmitting). This example will show you how to make a point-to-point link, using Dual Nstreme.
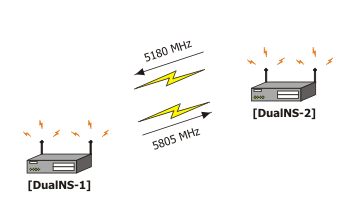
Configure DualNS-1:
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless> set 0,1 mode=nstreme-dual-slave
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:04:36 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050436" mode=nstreme-dual-slave ssid="MikroTik"
area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set
antenna-gain=0 frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default
rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
1 name="wlan2" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:28 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050028" mode=nstreme-dual-slave ssid="MikroTik"
area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set
antenna-gain=0 frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default
rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless> nstreme-dual
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless nstreme-dual> add rx-radio=wlan1 \
tx-radio=wlan2 rx-frequency=5180 tx-frequency=5805 disabled=no
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless nstreme-dual> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="nstreme1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:04:36 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no tx-radio=wlan2 rx-radio=wlan1
remote-mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 tx-band=5ghz tx-frequency=5805
rx-band=5ghz rx-frequency=5180 rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,54Mbps
framer-policy=none framer-limit=4000
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless nstreme-dual>
Note the MAC address of the interface nstreme1. You will need it to configure the remote (DualNS-2) router. As we have not configured the DualNS-2 router, we cannot define the remote-mac parameter on DualNS-1. We will do it after configuring DualNS-2!
The configuration of DualNS-2:
[admin@DualNS-2] interface wireless> set 0,1 mode=nstreme-dual-slave
[admin@DualNS-2] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050022" mode=nstreme-dual-slave ssid="MikroTik"
area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set
antenna-gain=0 frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default
rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
1 name="wlan2" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:06:B2 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C420506B2" mode=nstreme-dual-slave ssid="MikroTik"
area="" frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set
antenna-gain=0 frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default
rate-set=default supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=default disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@DualNS-2] interface wireless> nstreme-dual
[admin@DualNS-2] interface wireless nstreme-dual> add rx-radio=wlan1 \
\... tx-radio=wlan2 rx-frequency=5805 tx-frequency=5180 disabled=no \
\... remote-mac=00:0C:42:05:04:36
[admin@DualNS-2] interface wireless nstreme-dual> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="nstreme1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no tx-radio=wlan2 rx-radio=wlan1
remote-mac=00:0C:42:05:04:36 tx-band=5ghz tx-frequency=5180
rx-band=5ghz rx-frequency=5805 rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,54Mbps
framer-policy=none framer-limit=4000
[admin@DualNS-2] interface wireless nstreme-dual>
Now complete the configuration for DualNS-1:
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless nstreme-dual> set 0 remote-mac=00:0C:42:05:00:22
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless nstreme-dual> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="nstreme1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:04:36 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no tx-radio=wlan2 rx-radio=wlan1
remote-mac=00:0C:42:05:00:22 tx-band=5ghz tx-frequency=5805
rx-band=5ghz rx-frequency=5180 rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,54Mbps
framer-policy=none framer-limit=4000
[admin@DualNS-1] interface wireless nstreme-dual>
WEP Security
This example shows how to configure WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) on Access Point and Clients. In example we will configure an Access Point which will use 104bit-wep for one station and 40bit-wep for other clients. The configuration of stations is also present.
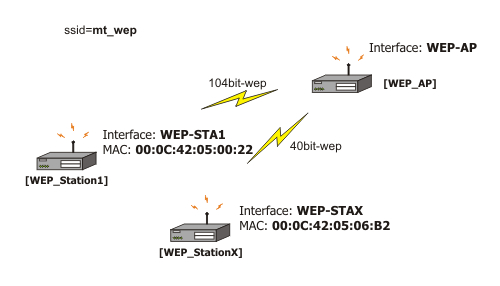
The key, used for connection between WEP_AP and WEP_Station1 will be 65432109876543210987654321, key for WEP_AP and WEP_StationX will be 1234567890!
Configure the Access Point:
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless security-profiles> add \
\... name=Station1 mode=static-keys-required static-sta-private-algo=104bit-wep \
\... static-sta-private-key=65432109876543210987654321
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless security-profiles> add name=StationX \
\... mode=static-keys-required static-algo-1=40bit-wep static-key-1=1234567890 \
\... static-transmit-key=key-1
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless security-profiles> print
0 name="default" mode=none wpa-unicast-ciphers="" wpa-group-ciphers=""
pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0="" static-algo-1=none
static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none
static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0 static-sta-private-algo=none
static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
1 name="Station1" mode=static-keys-required wpa-unicast-ciphers=""
wpa-group-ciphers="" pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0=""
static-algo-1=none static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2=""
static-algo-3=none static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0
static-sta-private-algo=104bit-wep
static-sta-private-key="65432109876543210987654321"
radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
2 name="StationX" mode=static-keys-required wpa-unicast-ciphers=""
wpa-group-ciphers="" pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0=""
static-algo-1=40bit-wep static-key-1="1234567890" static-algo-2=none
static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none static-key-3=""
static-transmit-key=key-1 static-sta-private-algo=none
static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless security-profiles> ..
[admin@MikroTik] interface wireless> set 0 name=WEP-AP mode=ap-bridge \
\... ssid=mt_wep frequency=5320 band=5ghz disabled=no security-profile=StationX
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="WEP-AP" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:04:36 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050436" mode=ap-bridge ssid="mt_wep" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=5320 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=StationX disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless> access-list
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless access-list> add private-algo=104bit-wep \
\... private-key=65432109876543210987654321 interface=WEP-AP forwarding=yes \
\... mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless access-list> print
Flags: X - disabled
0 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 interface=WEP-AP authentication=yes
forwarding=yes ap-tx-limit=0 client-tx-limit=0 private-algo=104bit-wep
private-key="65432109876543210987654321"
[admin@WEP_AP] interface wireless access-list>
Configure WEP_StationX:
[admin@WEP_Station1] interface wireless security-profiles> add name=Station1 \
\... mode=static-keys-required static-sta-private-algo=104bit-wep \
\... static-sta-private-key=65432109876543210987654321
[admin@WEP_Station1] interface wireless security-profiles> print
0 name="default" mode=none wpa-unicast-ciphers="" wpa-group-ciphers=""
pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0="" static-algo-1=none
static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none
static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0 static-sta-private-algo=none
static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
1 name="Station1" mode=static-keys-required wpa-unicast-ciphers=""
wpa-group-ciphers="" pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0=""
static-algo-1=none static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2=""
static-algo-3=none static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0
static-sta-private-algo=104bit-wep
static-sta-private-key="65432109876543210987654321"
radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
[admin@WEP_Station1] interface wireless security-profiles> ..
[admin@WEP_Station1] interface wireless> set wlan1 mode=station ssid=mt_wep \
\... band=5ghz security-profile=Station1 name=WEP-STA1 disabled=no
[admin@WEP_Station1] interface wireless> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="WEP-STA1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:00:22 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C42050022" mode=station ssid="mt_wep" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=Station1 disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@WEP_Station1] interface wireless>
Config of StationX:
[admin@WEP_StationX] interface wireless security-profiles> add name=StationX \
\... mode=static-keys-required static-algo-1=40bit-wep static-key-1=1234567890 \
\... static-transmit-key=key-1
[admin@WEP_StationX] interface wireless security-profiles> print
0 name="default" mode=none wpa-unicast-ciphers="" wpa-group-ciphers=""
pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0="" static-algo-1=none
static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none
static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0 static-sta-private-algo=none
static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
1 name="StationX" mode=static-keys-required wpa-unicast-ciphers=""
wpa-group-ciphers="" pre-shared-key="" static-algo-0=none static-key-0=""
static-algo-1=40bit-wep static-key-1="1234567890" static-algo-2=none
static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none static-key-3=""
static-transmit-key=key-1 static-sta-private-algo=none
static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m
[admin@WEP_StationX] interface wireless security-profiles> ..
[admin@WEP_StationX] interface wireless> set wlan1 name=WEP-STAX ssid=mt_wep \
\... band=5ghz security-profile=StationX mode=station disabled=no
[admin@WEP_StationX] interface wireless> print
0 R name="WEP-STAX" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0C:42:05:06:B2 arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5413
radio-name="000C420506B2" mode=station ssid="mt_wep" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power=default tx-power-mode=default
noise-floor-threshold=default periodic-calibration=default
burst-time=disabled fast-frames=no dfs-mode=none antenna-mode=ant-a
wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none wds-ignore-ssid=no
update-stats-interval=disabled default-authentication=yes
default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0 default-client-tx-limit=0
hide-ssid=no security-profile=StationX disconnect-timeout=3s
on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
[admin@WEP_StationX] interface wireless>
WPA Security
This example shows WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) configuration on Access Point and Client to secure all data which will be passed between AP and Client
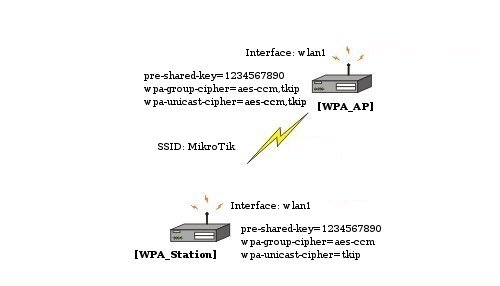
On the AP in default or in your own made profile as an encryption algorithm choose wpa-psk. Specify the pre-shared-key, wpa-unicast-ciphers and wpa-group-cipher
[admin@WPA_AP] interface wireless security-profiles> set default mode=wpa-psk\ \... pre-shared-key=1234567890 wpa-unicast-ciphers=aes-ccm,tkip wpa-group-ciphers=aes-ccm,tkip [admin@WPA_AP] interface wireless security-profiles> pr 0 name="default" mode=wpa-psk wpa-unicast-ciphers=tkip,aes-ccm wpa-group-ciphers=tkip,aes-ccm pre-shared-key="1234567890" static-algo-0=none static-key-0="" static-algo-1=none static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0 static-sta-private-algo=none static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m [admin@WPA_AP] interface wireless security-profiles>
On the Client do the same. Encryption algorithm, wpa-group-cipher and pre-shared-key must be the same as specified on AP, wpa-unicast-cipher must be one of the ciphers supported by Access Point
[admin@WPA_Station] interface wireless security-profiles> set default mode=wpa-psk\ \... pre-shared-key=1234567890 wpa-unicast-ciphers=tkip wpa-group-ciphers=aes-ccm,tkip [admin@WPA_Station] interface wireless security-profiles> pr 0 name="default" mode=wpa-psk wpa-unicast-ciphers=tkip wpa-group-ciphers=tkip,aes-ccm pre-shared-key="1234567890" static-algo-0=none static-key-0="" static-algo-1=none static-key-1="" static-algo-2=none static-key-2="" static-algo-3=none static-key-3="" static-transmit-key=key-0 static-sta-private-algo=none static-sta-private-key="" radius-mac-authentication=no group-key-update=5m [admin@WPA_Station] interface wireless security-profiles>
Test the link between Access point and the client
[admin@WPA_Station] interface wireless > print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="wlan1" mtu=1500 mac-address=00:0B:6B:35:E5:5C arp=enabled
disable-running-check=no interface-type=Atheros AR5213
radio-name="000B6B35E55C" mode=station ssid="MikroTik" area=""
frequency-mode=superchannel country=no_country_set antenna-gain=0
frequency=5180 band=5ghz scan-list=default rate-set=default
supported-rates-b=1Mbps,2Mbps,5.5Mbps,11Mbps
supported-rates-a/g=6Mbps,9Mbps,12Mbps,18Mbps,24Mbps,36Mbps,48Mbps,
54Mbps
basic-rates-b=1Mbps basic-rates-a/g=6Mbps max-station-count=2007
ack-timeout=dynamic tx-power-mode=default noise-floor-threshold=default
periodic-calibration=default burst-time=disabled dfs-mode=none
antenna-mode=ant-a wds-mode=disabled wds-default-bridge=none
wds-ignore-ssid=no update-stats-interval=disabled
default-authentication=yes default-forwarding=yes default-ap-tx-limit=0
default-client-tx-limit=0 hide-ssid=no security-profile=default
disconnect-timeout=3s on-fail-retry-time=100ms preamble-mode=both
compression=no allow-sharedkey=no
[admin@WPA_Station] interface wireless >
Troubleshooting
Description
-
If I use WDS and DFS, the routers do not connect to each other!
As the WDS routers must operate at the same frequency, it is very probable that DFS will not select the frequency that is used by the peer router.
-
MikroTik RouterOS does not send any traffic through Cisco Wireless Access Point or Wireless Bridge
If you use CISCO/Aironet Wireless Ethernet Bridge or Access Point, you should set the Configuration/Radio/I80211/Extended (Allow proprietary extensions) to off, and the Configuration/Radio/I80211/Extended/Encapsulation (Default encapsulation method) to RFC1042. If left to the default on and 802.1H, respectively, you won't be able to pass traffic through the bridge.
-
Prism wireless clients don't connect to AP after upgrade to 2.9
Prism wireless card's primary firmware version has to be at least 1.0.7 in order to boot wireless card's secondary firmware, which allows Prism card correctly operate under RouterOS. Check the log file to see whether the wireless card's secondary firmware was booted.
-
Prism wireless clients don't connect to AP
Prism wireless clients do not connect to AP that work with enabled hide-ssid feature