Features include:
[MikroTik] bridge> ?
Configure interfaces that are used for bridge forwarding, protocols that will
be forwarded and look at bridge forwarding table.
export print configuration as set of router commands
get get value of property
host Bridge forwarding table
interface Interfaces used for bridging
print print settings
set change settings
[MikroTik] bridge> print
ip: discard
ipx: discard
appletalk: discard
ipv6: discard
arp: discard
other: discard
priority: 1
[MikroTik] bridge>
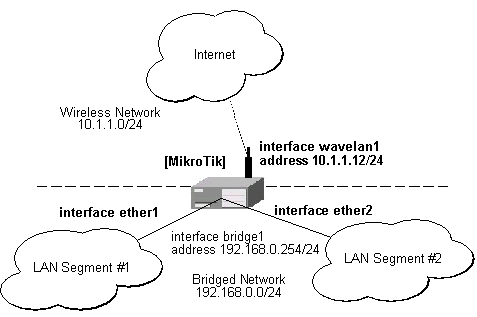
Assume we want to enable bridging between two Ethernet LAN segments and have the MikroTik router be the default gateway for them:

When configuring the MikroTik router for bridging you should do the following:
When configuring the bridge settings, each protocol that should be forwarded should be set to 'forward'. The 'other' protocol includes all protocols not listed before:
[MikroTik] bridge> set ip=forward arp=forward other=forward
[MikroTik] bridge> print
ip: forward
ipx: discard
appletalk: discard
ipv6: discard
arp: forward
other: forward
priority: 1
[MikroTik] bridge>
The priority argument is used by the Spanning Tree Protocol to determine, which port remains enabled if two ports form a loop.
Next, each interface that should be included in the bridging table should be set to 'forward=yes':
[MikroTik] bridge interface> print Flags: X - disabled # INTERFACE 0 X ether2 1 X ether1 [MikroTik] bridge interface> enable 0 [MikroTik] bridge interface> enable 1 [MikroTik] bridge interface> print # INTERFACE 0 ether2 1 ether1 [MikroTik] bridge interface>
After setting some interface for bridging, a bridge interface is added to the router's interfaces table. You should enable the interface in order to start using it:
[MikroTik] bridge interface> /interface [MikroTik] interface> print Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic # NAME MTU TYPE 0 ether2 1500 ether 1 ether1 1500 ether 2 wavelan1 1500 wavelan 3 X pppoe-out1 1492 pppoe-out 4 X bridge1 1500 bridge [MikroTik] interface> enable bridge1 [MikroTik] interface> print Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic # NAME MTU TYPE 0 ether2 1500 ether 1 ether1 1500 ether 2 wavelan1 1500 wavelan 3 X pppoe-out1 1492 pppoe-out 4 bridge1 1500 bridge [MikroTik] interface> bridge print Flags: X - disabled # NAME MAC-ADDRESS 0 bridge1 FE:FD:08:00:9A:CB [MikroTik] interface>
If you want to access the router through unnumbered bridged interfaces, it is required to add an IP address to the 'bridge' interface:
[MikroTik] ip address> add address=192.168.0.254/24 interface=bridge1 [MikroTik] ip address> add address=10.1.1.12/24 interface=wavelan1 [MikroTik] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 bridge1 1 10.1.1.12/24 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.255 wavelan1 [MikroTik] ip address>
The hosts on LAN segments #1 and #2 should use IP addresses from the same network 192.168.0.0/24 and have the default gateway set to 192.168.0.254 (MikroTik router).
Bridge Monitoring
The bridge can be monitored in real time.
The bridging table shows the MAC address of hosts,
interface which can forward packets to the host,
and the age of the information shown in seconds:
[MikroTik] bridge host> print Flags: L - local MAC-ADDRESS ON-INTERFACE AGE 00:00:21:84:88:81 ether1 0s L 00:00:B4:5D:7C:68 ether1 0s 00:00:B4:C6:80:EA eoip-tunnel1 49s 00:30:4F:12:81:F0 eoip-tunnel1 3m59s 00:30:4F:12:84:F8 eoip-tunnel1 2m55s 00:30:84:0A:58:B7 ether1 12s 00:90:27:45:26:CD ether1 1m14s 00:90:27:6A:A1:2E ether1 1m14s 00:A0:24:C8:07:E6 ether1 4m14s 00:A0:C9:1C:E4:9B ether1 1m30s 00:A0:C9:3D:50:08 ether1 4m4s 00:C0:DF:E6:A7:43 ether1 1m30s 00:C0:DF:ED:FA:2C ether1 4m14s L FE:FD:00:00:00:00 eoip-tunnel1 0s [MikroTik] bridge host>